How to Prepare for the World Transformed by Quantum Computers
Technology is constantly evolving, and quantum computing is one of the most groundbreaking fields. Unlike classical computers, which use binary bits (0s and 1s), quantum computers harness quantum bits (qubits), allowing them to perform complex calculations exponentially faster than today’s devices.
As quantum breakthroughs continue, industries ranging from cryptography to drug discovery and climate modelling stand to be transformed. With such immense potential, governments and tech giants are investing billions in quantum research. But what makes quantum computers so powerful, and how will they shape the future? Let’s find out.
Key Benefits: Why Quantum Computing Matters

Revolutionizing Industries
Quantum computing is expected to change various sectors profoundly, solving problems currently impossible for classical computers.
1. Cryptography and Cybersecurity
- Quantum computers can break traditional encryption within seconds, posing a significant cybersecurity challenge.
- However, quantum cryptography offers unbreakable security, ensuring safer data transmission through quantum key distribution (QKD).
2. Healthcare and Drug Discovery
- Quantum simulations model molecular interactions at the atomic level, accelerating drug discovery.
- This could lead to personalised medicine, better treatments, and even potential cures for incurable diseases.
3. Financial Optimization
- Quantum computing enhances risk assessment, fraud detection, and investment strategies.
- Banks and hedge funds can optimise complex financial models, leading to more stable and efficient markets.
4. Climate Science & Environmental Solutions
- Quantum-powered climate models improve accuracy in predicting extreme weather and assessing environmental impact.
- Quantum computing helps develop materials for better batteries and sustainable energy solutions.
Pro Tip:
Governments and industries are preparing for post-quantum cryptography (PQC) to ensure data security when quantum computers become commercially viable.
Quick Guide: How Quantum Computers Work
Understanding Quantum Mechanics
To grasp quantum computing, two key principles of quantum mechanics must be understood:
1. Superposition
- Qubits can exist in multiple states simultaneously, unlike classical bits, which are either 0 or 1.
- This enables quantum computers to process many calculations simultaneously, exponentially increasing computational power.
2. Entanglement
- Qubits can be entangled, meaning that the state of one qubit instantly influences another, no matter how far apart they are.
- This property enables faster processing and ultra-secure quantum communication.
Quantum Gates and Circuits
Quantum gates manipulate qubits similarly to classical logic gates, but they enable multiple calculations in parallel, solving problems in ways that classical computers cannot.
Important Tip:
If you’re new to quantum computing, explore cloud-based quantum simulators like IBM Quantum Experience or Google Cirq.
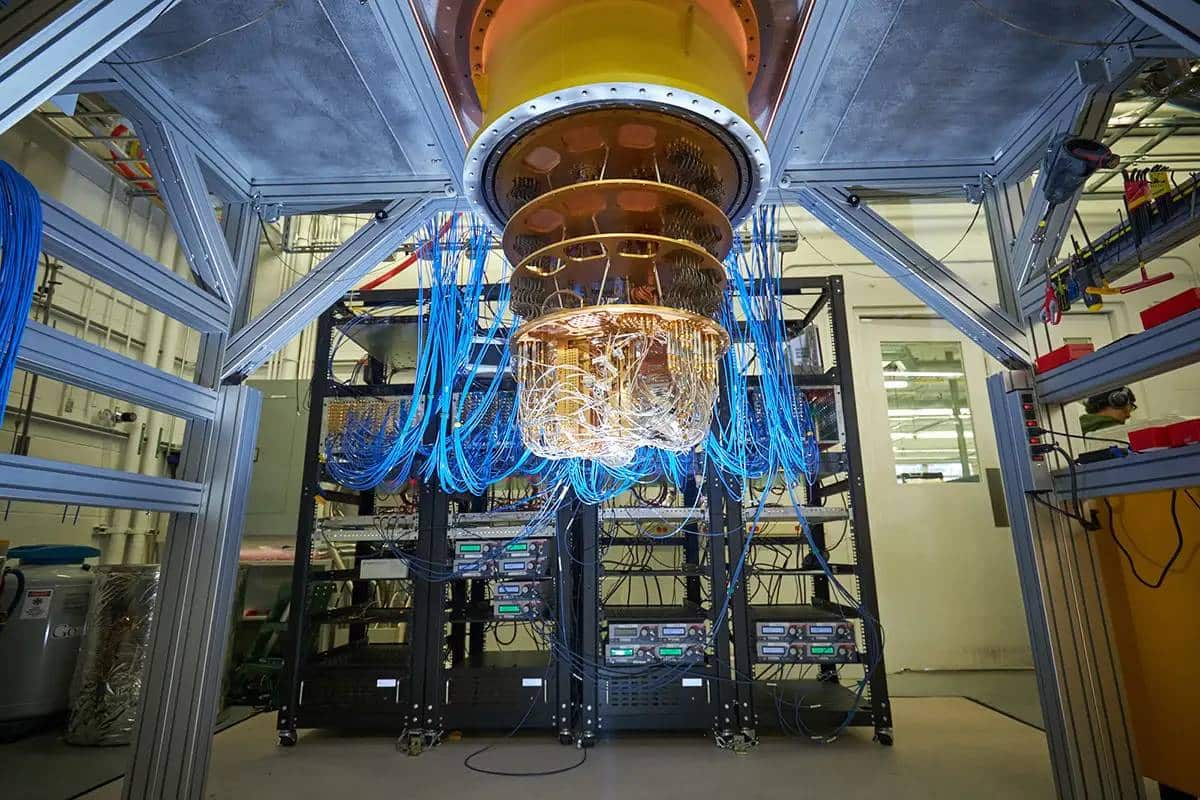
Top Quantum Processors Leading the Industry
1. IBM’s Quantum Processor
- IBM Eagle (127 qubits) is one of the most advanced processors.
- IBM provides cloud-based access to quantum computing through IBM Quantum Experience.
2. Google’s Sycamore Processor
- Achieved quantum supremacy in 2019, solving a problem in 200 seconds that would take a supercomputer 10,000 years.
- Built to tackle highly complex problems beyond classical computing capabilities.
3. Rigetti’s Aspen Processor
- Focuses on hybrid quantum-classical computing.
- Designed to integrate quantum processing into existing computing workflows.
Best Practices & Common Mistakes in Quantum Computing
Best Practices
- Stay updated on the latest quantum breakthroughs through conferences, research papers, and online forums.
- Experiment with cloud-based quantum platforms like IBM Quantum, Google Cirq, and Amazon Bracket.
- Explore hybrid solutions combining classical and quantum computing for enhanced efficiency.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Thinking quantum computers are just faster versions of classical computers — they work fundamentally differently.
Underestimating the challenges of quantum error correction — quantum systems still face issues with stability and noise.
Ignoring the need for quantum-safe encryption — organisations must prepare for a future where classical cryptography becomes obsolete.
Advanced Insights: The Future of Quantum Computing

1. Fault-Tolerant Quantum Computing
One of the biggest hurdles in quantum computing is error correction. Researchers are working on fault-tolerant quantum systems that allow reliable, large-scale calculations.
2. Industry Collaborations & Roadmaps
- Tech leaders like IBM, Google, and Microsoft partner with governments and universities to accelerate quantum advancements.
- The Quantum Economic Development Consortium (QED-C) is developing global quantum research and commercialisation roadmaps.
3. Quantum Computing in AI & Machine Learning
- Quantum AI could revolutionise machine learning by processing vast datasets at unimaginable speeds.
- Quantum-enhanced AI models may lead to more powerful and efficient neural networks.
Secret Tip:
To gain hands-on experience, start learning quantum programming languages like Qiskit (IBM), Cirq (Google), or Bracket (Amazon).
Frequently Asked Questions about Quantum Computing
- Will quantum computers replace classical computers?
- How close are we to commercial quantum computers?
- Who is leading the quantum computing race?
- What industries will benefit most from quantum computing?
- Can I access a quantum computer today?
- How will quantum computing impact your field?
No, quantum computers are designed to complement classical systems. They specialise in solving highly complex problems, but classical computers remain essential for everyday tasks.
Large-scale, error-free quantum computers could take another 10-20 years, but early quantum applications are already being developed.
Companies like IBM, Google, Microsoft, and Rigetti, along with government-funded research programs worldwide, are leading the race.
Cryptography, pharmaceuticals, finance, AI, climate modelling, and material science stand to gain the most.
Yes! Cloud-based quantum platforms like IBM Quantum, Google Cirq, and Amazon Bracket allow researchers and developers to experiment with quantum computing today.
Join the conversation and explore how this groundbreaking technology could shape the future!
The Quantum Revolution is Here
Quantum computing is no longer just a theoretical concept—it is a rapidly evolving field with the potential to redefine industries, solve complex global challenges, and unlock new technological frontiers.
While challenges remain, the progress being made is significant. Researchers and industry leaders work tirelessly to make quantum computing scalable, reliable, and accessible. As this technology matures, it will complement classical computing, bringing faster problem-solving capabilities and innovations.
“We are on the brink of a new era in computing—one where quantum mechanics will reshape our understanding of data processing, security, and scientific discovery.”