The Technology Blog
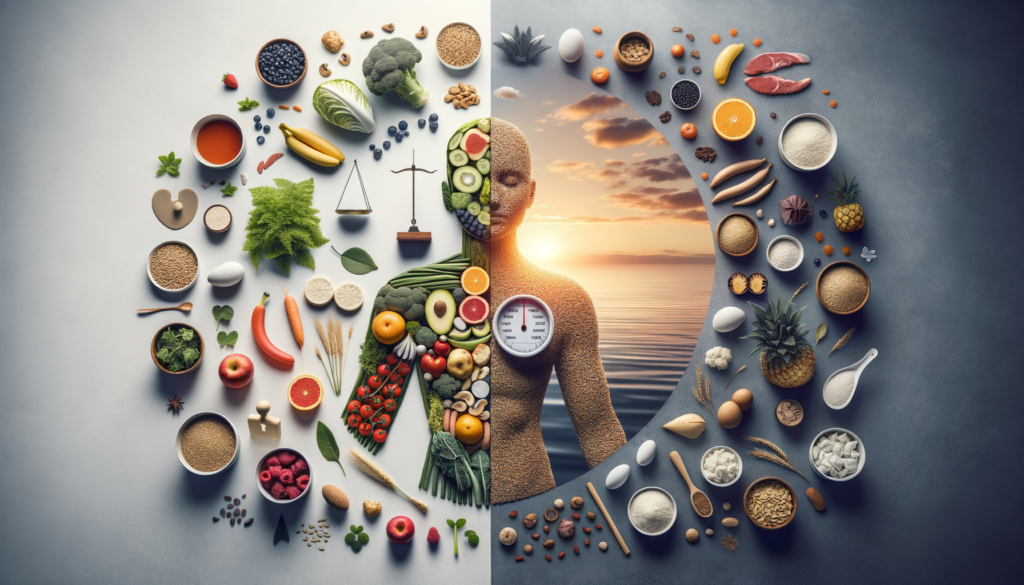

Can Food Affect Your Mood? Exploring Nutrients Linked to Emotional Well-Being
The Role of Nutrients in Emotional Health
In recent years, the relationship between what we eat and our mental health has become a focal point in both scientific research and public interest. While food alone cannot cure mental health disorders, it is increasingly recognized that certain nutrients can play a supportive role in maintaining emotional well-being. Essential nutrients such as omega-3 fatty acids, B vitamins, and amino acids are crucial for brain health and neurotransmitter function. These substances are involved in the production of serotonin and dopamine, chemicals in the brain that regulate mood and emotion.
Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, are particularly noted for their anti-inflammatory properties and their role in brain cell membrane function. Studies suggest that individuals with lower levels of omega-3s may experience mood disorders more frequently. Similarly, B vitamins, which are abundant in whole grains, eggs, and leafy greens, are vital for energy production and neurotransmitter synthesis. A deficiency in these vitamins can lead to fatigue and mood swings.
Moreover, the amino acid tryptophan, found in turkey, chicken, and legumes, is a precursor to serotonin. Adequate intake of tryptophan can help in maintaining balanced serotonin levels, which is associated with a stable mood. Including these nutrients in your diet may not only support your physical health but also contribute to a more balanced emotional state.
How Gut Health Influences Mood
The gut-brain connection is a fascinating area of study that highlights how our digestive system interacts with our mental health. The gut microbiome, a complex community of microorganisms living in our intestines, plays a significant role in this relationship. These microorganisms produce neurotransmitters like serotonin, which is often referred to as the “feel-good” hormone. In fact, about 90% of serotonin is produced in the gut.
A balanced diet rich in fiber, probiotics, and prebiotics can help maintain a healthy gut microbiome. Foods such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and other fermented products are excellent sources of probiotics. Prebiotics, found in foods like bananas, onions, and garlic, serve as food for these beneficial bacteria. By promoting a healthy gut environment, these foods can potentially enhance mood and reduce anxiety.
Research has shown that individuals with a diverse gut microbiome tend to have lower levels of stress and anxiety. This suggests that fostering a healthy gut can have a positive impact on emotional health. Therefore, paying attention to gut health through dietary choices can be an effective strategy in supporting mental well-being.
Practical Dietary Tips for Emotional Well-Being
Incorporating foods that support emotional health into your daily routine doesn’t have to be complicated. Here are some practical tips to help you get started:
- Include a variety of fruits and vegetables: These are packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support brain health.
- Opt for whole grains: Foods like quinoa, brown rice, and oats provide B vitamins and fiber, promoting energy and gut health.
- Choose lean proteins: Sources such as chicken, fish, and legumes supply essential amino acids necessary for neurotransmitter production.
- Incorporate healthy fats: Avocados, nuts, and olive oil are rich in omega-3s and monounsaturated fats, crucial for brain function.
- Stay hydrated: Proper hydration is essential for overall health and can influence mood and concentration levels.
By making these dietary adjustments, you can create a supportive environment for your mental well-being. Remember, while food can play a significant role in emotional health, it is one piece of the puzzle. Combining a nutritious diet with regular physical activity, sufficient sleep, and stress management strategies can lead to a more balanced and fulfilling life.